Devices for the protection of low voltage lines
REQUEST MORE INFORMATION
INTERNAL PROTECTION - TRANSIENT SURGES
The voltage surges are elevations in voltage that can occur in electrical distribution, data communications, and telephony lines resulting in premature aging of components and/or damage to the equipment connected to the network. Overvoltages caused by direct lightning, indirect, disconnection of inductive loads (coils, motors, etc ...), network switches, and/or defects in them.
Overvoltage surges are large spikes with a slope and are short-lived, yet the strong effects on sensitive electronic equipment are devastating.
The level of the voltage that can appear on the network is a function of the isoceraúnico area level (lightning/year • Km2), the type of attack, aerial or underground, and the proximity of the MV / LV transformer.
For proper equipment protection, a low-resistance grounding system should be implemented and equipotentially connected to the external protection system. Additionally, surge protection devices should be installed on all supply lines (power, telephone, data, etc.).
Installation of external lightning protection (according to IEC 62305-3) and surge arresters (according to IEC 62305-4) significantly reduces the risk of damage caused by lightning in structures, equipment, and people (calculation risks according to IEC 62305-2).
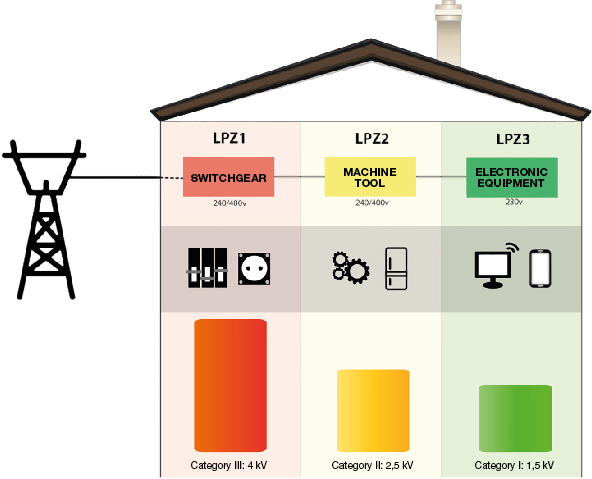
surge categories
The categories indicate what the value of voltage shock wave to withstand for the equipment and determine the maximum value of residual voltage Up which should have surge protectors in each area.
The purpose of installing surge protectors is to avoid the devastating effects of surges on electrical and/or electronic equipment, cutting these peaks to permissible values as per RBT ITC-23, depending on the category that the equipment wants to be protected
THE IMPORTANCE OF PROTECTION
An unprotected structure can face numerous short- and long-term problems, as major failures may occur suddenly in devices connected to the electrical network, potentially leading to the complete destruction of the electrical system of the affected equipment. Most importantly, proper protection ensures the safety of people inside the structure at the moment a voltage spike occurs.
Not all overvoltages are noticeable or immediately perceptible. Some are minor and do not cause visible damage right away, but they gradually shorten the lifespan of connected devices over time.
By installing transient surge protectors, you ensure the longevity and proper operation of machines and devices, whether in residential or industrial settings. When an overvoltage occurs, the protector performs its function by diverting the surge safely to the grounding system without interrupting the power supply of the installation.
As a safety device, it is essential that the surge suppressor is certified and complies with current standards. A malfunction could have serious consequences for the installation. This is why INGESCO protectors are tested and certified to guarantee their full and proper performance.
selection of surge protectors
Surge protectors are connected between an active conductor (phase) and ground, upstream of the equipment they protect.
Normal impedance is high, but when the voltage exceeds the threshold voltage, the protector becomes a low-impedance ground to dissipate the surge, protecting the equipment.
To select which protector to install, we must consider:
- Nominal line voltage.
- Number of phases to be protected.
- Type of network (TT, TN, TNC, SCNT).
- Category of equipment to be protected.
- Level of exposure to surges (Imax).
standards
Surge protection devices must conform to the following standards:
- UNE EN 61643-11:2013 Low voltage surge protection devices.
- IEC 62305 series – Lightning protection:
- IEC 62305-1: Protection against lightning - General principles.
- IEC 62305-2: Protection against lightning –Risk management.
- IEC 62305-3: Protection against lightning – Physical damage to structure and life hazard.
- IEC 62305-4: Protection against lightning – Electrical and electronic systems within structures.
- UNE 21186:2011 /NF C 17-102:2011 Protection against lightning: Lightning rods with early stream emitters.
- UNE EN 60664-1 Isolation coordination for low voltage equipment systems (networks).





